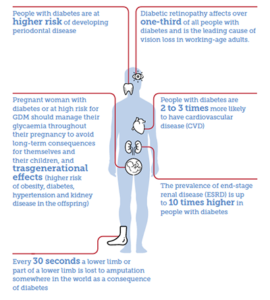
According to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), People with diabetes are at greater risk of developing a number of serious health problems and complications related to among others:- cardiovascular disease, blindness, heart, eyes, nerves and teeth disease, in addition to kidney failure, and lower limb (Leg or foot) amputation.
Cardiovascular disease:
Cardiovascular disease is the most common cause of death in people with diabetes, says the IDF. The disease affects the heart and blood vessels and may cause deadly complications such as coronary artery disease leading to heart attack and stroke. This happened due to the hardening, narrowing or blocking of blood vessels or arteries supplying the heart with blood due to build-up of cholesterol and other material, called plaque.
Kidney disease (diabetic nephropathy):
The IDF adds that kidney disease is much more common in people with diabetes than in those without the disease. It is caused by damage to small blood vessels in the kidneys leading to the kidneys not being able to do their work or to fail altogether. Maintaining near normal levels of blood glucose and blood pressure can greatly reduce the risk of kidney disease.
Nerve disease (diabetic neuropathy):
People with diabetes carry a risk of amputation (cutting of legs or feet) that may be more than 25 times greater than that of people without diabetes.
This is because diabetes can cause damage to the nerves throughout the body when blood glucose and blood pressure are too high. This can lead to problems with digestion, erectile dysfunction, and in particular the feet.
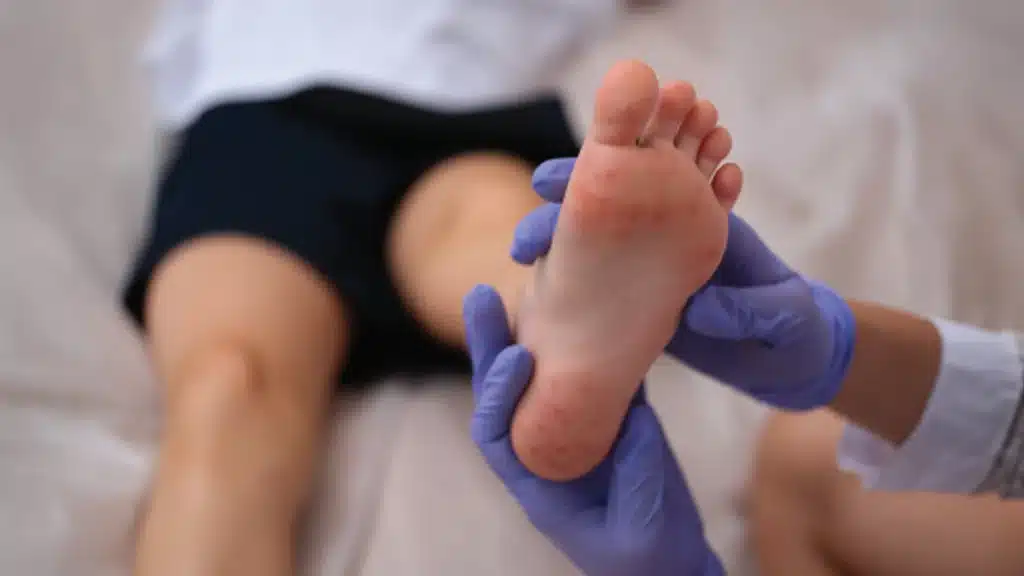
Nerve damage in these areas can lead to pain, tingling, and loss of feeling, leading to serious infections and possible amputations as injuries go unnoticed.
For this reason, people with diabetes should regularly examine their feet for injuries or cracked skin which may allow infection into the body.
Eye disease (diabetic retinopathy):
The IDF maintains that most people with diabetes will develop some form of eye disease (retinopathy) causing reducing their ability to see or blindness. However, this can be managed through regular eye check-ups and keeping glucose levels at or close to normal.
Pregnancy complications:
Women with any type of diabetes during pregnancy risk a number of complications if they do not carefully monitor and manage their condition. These include: – possible organ damage to the unborn baby. And the unborn baby putting on excess weight which can lead to problems during delivery.
Oral (mouth) complications:
People with diabetes have an increased risk of losing their teeth due to inflammation of the gums (periodontitis) if blood glucose is not properly managed. Yearly visits to the dentist are recommended for symptoms of gum disease such as bleeding when brushing teeth or swollen gums.
Complications at a Glance
Source: International Diabetes Federation